Spring AOP?
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public ExecutionTimerAspect executionTimerAspect() {
return new ExecutionTimerAspect();
}
}- aop를 제공하기 위한 스프링 프레임워크의 모듈
- 프록시 기반의 aop를 지원
- 컴파일 시점에 코드에 공통 기능
- 설정 클래스에
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy를 명시함으로써 활성화 가능 - 스프링 컨테이너에서 관리하는 빈에만 적용 가능
Note
aop의 기본 개념은 핵심 기능에 공통 기능을 삽입하는 것이다. 즉 핵심 기능의 코드를 수정하지 않으면서 공통 기능의 구현을 추가하는 것이 aop이다. 핵심 기능에 공통 기능을 삽입하는 방법에는 다음 세 가지가 있다.
- 컴파일 시점에 코드에 공통 기능을 삽입하는 방법
- 클래스 로딩 시점에 바이트 코드에 공통 기능을 삽입하는 방법
- 런타임에 프록시 객체를 생성해서 공통 기능을 삽입하는 방법
첫 번째 방법은 aop 개발 도구가 소스 코드를 컴파일 하기 전에 공통 구현 코드를 소스에 삽입하는 방식으로 동작한다. 두 번째 방법은 클래스를 로딩할 때 바이트 코드에 공통 기능을 클래스에 삽입하는 방식으로 동작한다. 이 두 가지는 스프링 aop에서는 지원하지 않으며 aspectj와 같이 aop 전용 도구를 사용해서 적용할 수 있다.
Proxy
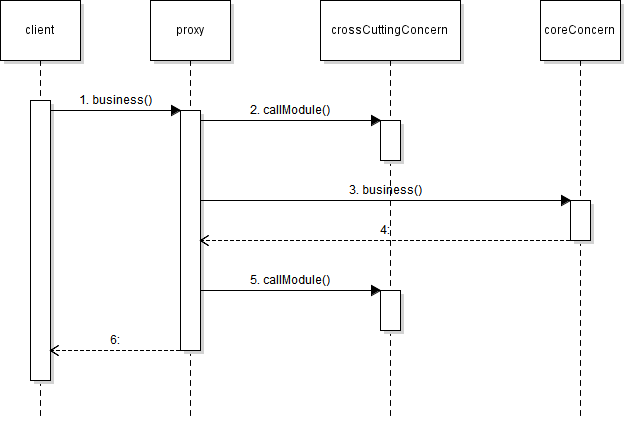
- 핵심 기능의 실행은 다른 객체에 위임하고 부가적인 기능을 제공하는 객체
- 핵심 기능을 구현하지 않는 대신 여러 객체에 공통으로 적용할 수 있는 기능을 구현
- 실제 핵심 기능을 실행하는 객체는 대상 객체라고 부름
- 프록시를 이용해 aop를 구현하는 스프링은 메서드 실행만을
JoinPoint로 인식- 런타임에 메서드 호출만 가로챌 수 있음
- 대상 객체의
public메서드만이 프록싱 대상이 됨public이외의 메서드까지 aop를 적용하고 싶다면 aspectj를 사용해야 함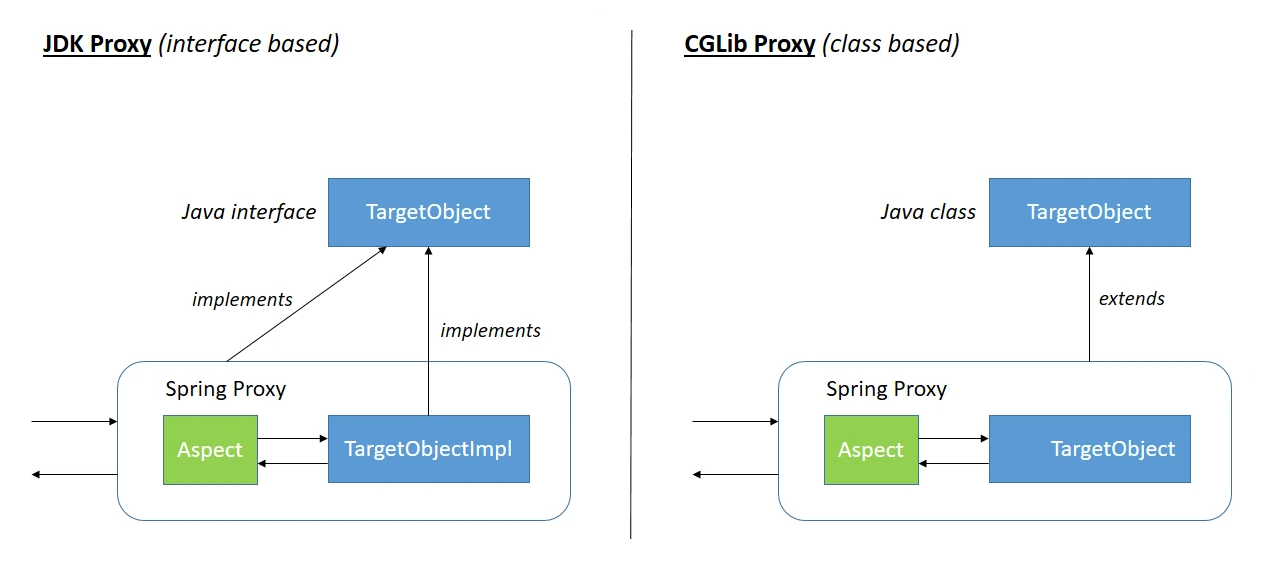
- 대상 객체가 하나 이상의 인터페이스를 구현하는 경우, jdk 동적 프록시를 사용하여 인터페이스를 구현한 프록시 객체를 생성
- 대상 객체가 인터페이스를 구현하지 않은 경우,
CGLIB를 사용하여 대상 클래스를 상속한 프록시 객체를 생성 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy의proxyTargetClass속성을true로 설정하면, 인터페이스를 구현한 객체라도CGLIB를 사용하여 대상 클래스를 상속한 프록시가 생성됨
- 대상 객체가 인터페이스를 구현하지 않은 경우,
Advice
- 언제 공통 관심 기능을 핵심 로직에 적용할 지를 정의
- 메서드를 호출하기 전(언제)에 트랜잭션 시작(공통 기능)을 적용
@Pointcut에 여러 advice가 적용될 수 있음- 어떤
@Aspect가 먼저 적용될지는 스프링 프레임워크나 자바 버전에 따라 달라질 수 있기 때문에 적용 순서가 중요하다면@Order를 사용하여 직접 순서를 지정
- 어떤
@Pointcut을 따로 선언하지 않고, advice에서@Pointcut의execution표현식을 직접 지정할 수 있음
@Before
@Aspect
public class ExecutionTimerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.service..*(..))")
private void publicTarget() { }
@Before("publicTarget()")
public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature sig = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.printf("%s.%s(%s) 실행 전\n",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
sig.getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
}- 대상 객체의 메서드 호출 전에 공통 기능을 실행
@After
@Aspect
public class ExecutionTimerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.service..*(..))")
private void publicTarget() { }
@After("publicTarget()")
public void afterAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature sig = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.printf("%s.%s(%s) 실행 후\n",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
sig.getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
}Exception발생 여부에 상관없이 대상 객체의 메서드 실행 후 공통 기능을 실행
@AfterReturning
@Aspect
public class ExecutionTimerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.service..*(..))")
private void publicTarget() { }
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "publicTarget()", returning = "result")
public void afterReturningAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
Signature sig = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.printf("%s.%s(%s) 정상 실행 후 결과: %s\n",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
sig.getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()), result);
}
}- 대상 객체의 메서드가
Exception없이 실행된 이후에 공통 기능을 실행
@AfterThrwoing
@Aspect
public class ExecutionTimerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.service..*(..))")
private void publicTarget() { }
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "publicTarget()", throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowingAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex) {
Signature sig = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.printf("%s.%s(%s) 실행 중 예외 발생: %s\n",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
sig.getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()), ex.getMessage());
}
}- 대상 객체의 메서드를 실행하는 도중
Exception이 발생한 경우에 공통 기능을 실행
@Around
@Aspect
public class ExecutionTimerAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.service..*(..))")
private void publicTarget() { }
@Around("publicTarget()")
public Object measure(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 대상 객체의 메서드 실행
return result;
} finally {
long finish = System.nanoTime();
Signature sig = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.printf(
"%s.%s(%s) 실행 시간: %d ns\n",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
sig.getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()),
(finish - start));
}
}
}- 대상 객체의 메서드 실행 전, 후 또는
Exception발생 시점에 공통 기능을 실행- 다양한 시점에 원하는 기능을 삽입할 수 있기 때문에 가장 많이 사용되는 방식